PPT Transverse Wave PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6075233
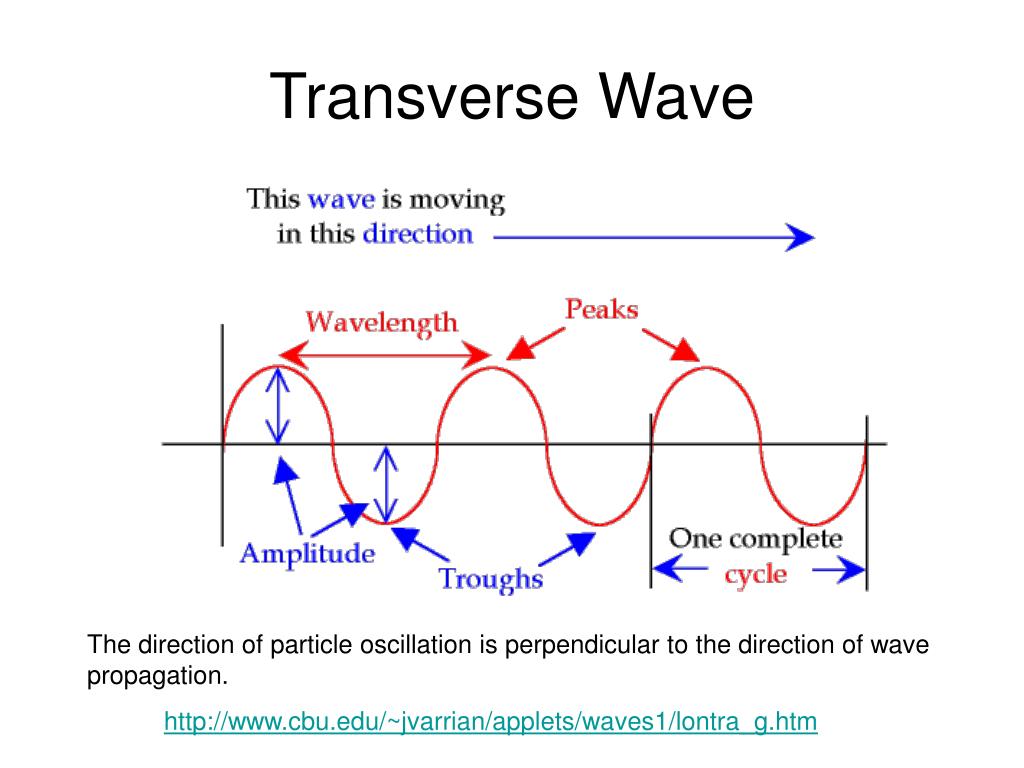
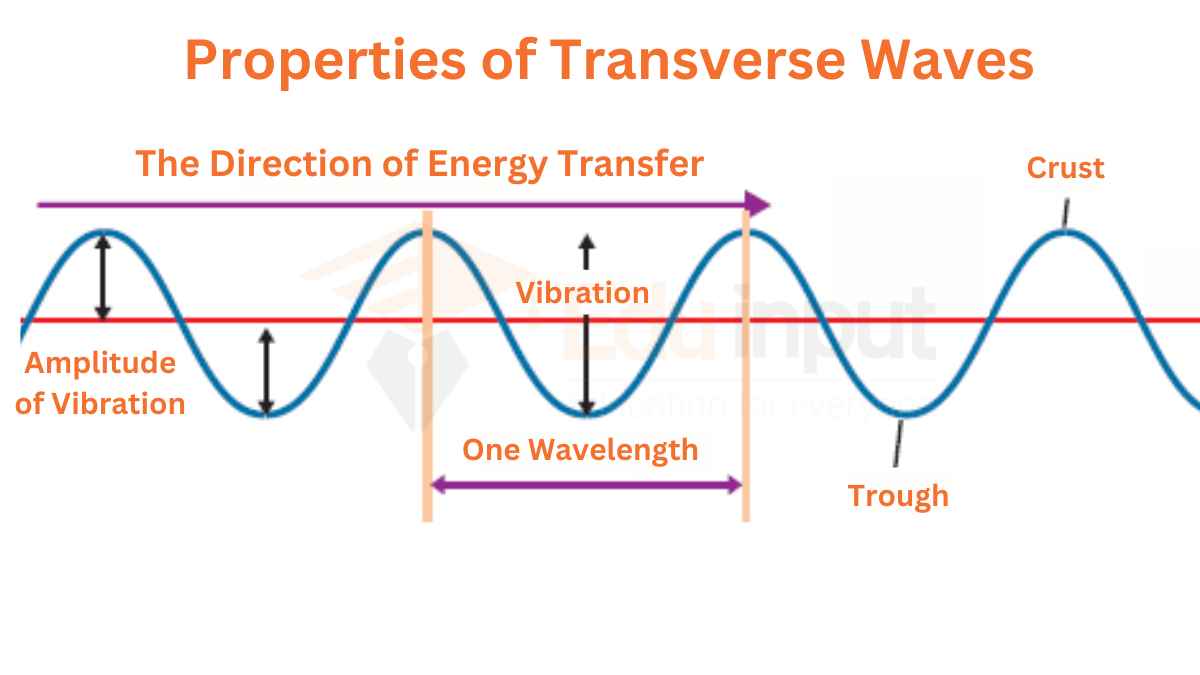
Transverse waves Transverse waves vibrate the particles of a medium perpendicularly to the direction of wave travel to produce the features shown in Figure 1 below. Figure 1: Parts of a transverse wave. [What's the difference between the crest and the amplitude?] Longitudinal waves

Draw and label a diagram of a transverse wave. Diagram Quizlet
The Simple Wave Simulator Interactive provides the learner with a virtual wave machine for exploring the nature of a wave, quantitative relationships between wavelength, frequency and speed, and comparisons between transverse waves such as those traveling through a rope and longitudinal waves such as sound.

For a transverse wave, the _________ depends on the distance from the rest position to a crest
A transverse wave is defined as a wave where the movement of the particles of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of the propagation of the wave. shows this in a diagram. In this case, the medium through which the waves propagate is the rope. The wave traveled from one end to the other, while the rope moved up and down.
Transverse WavesExamples, Diagram, And Properties
A transverse wave propagates so that the disturbance is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. An example of a transverse wave is shown in Figure 13.3, where a woman moves a toy spring up and down, generating waves that propagate away from herself in the horizontal direction while disturbing the toy spring in the vertical direction.

Waves Class 11 Notes, Formulas, NCERT, For NEET Leverage Edu
Anne Schmidt Learn how to QUICKLY label a transverse wave with crest, trough, wavelength, frequency, amplitude, resting position and resting points. We will also learn h.
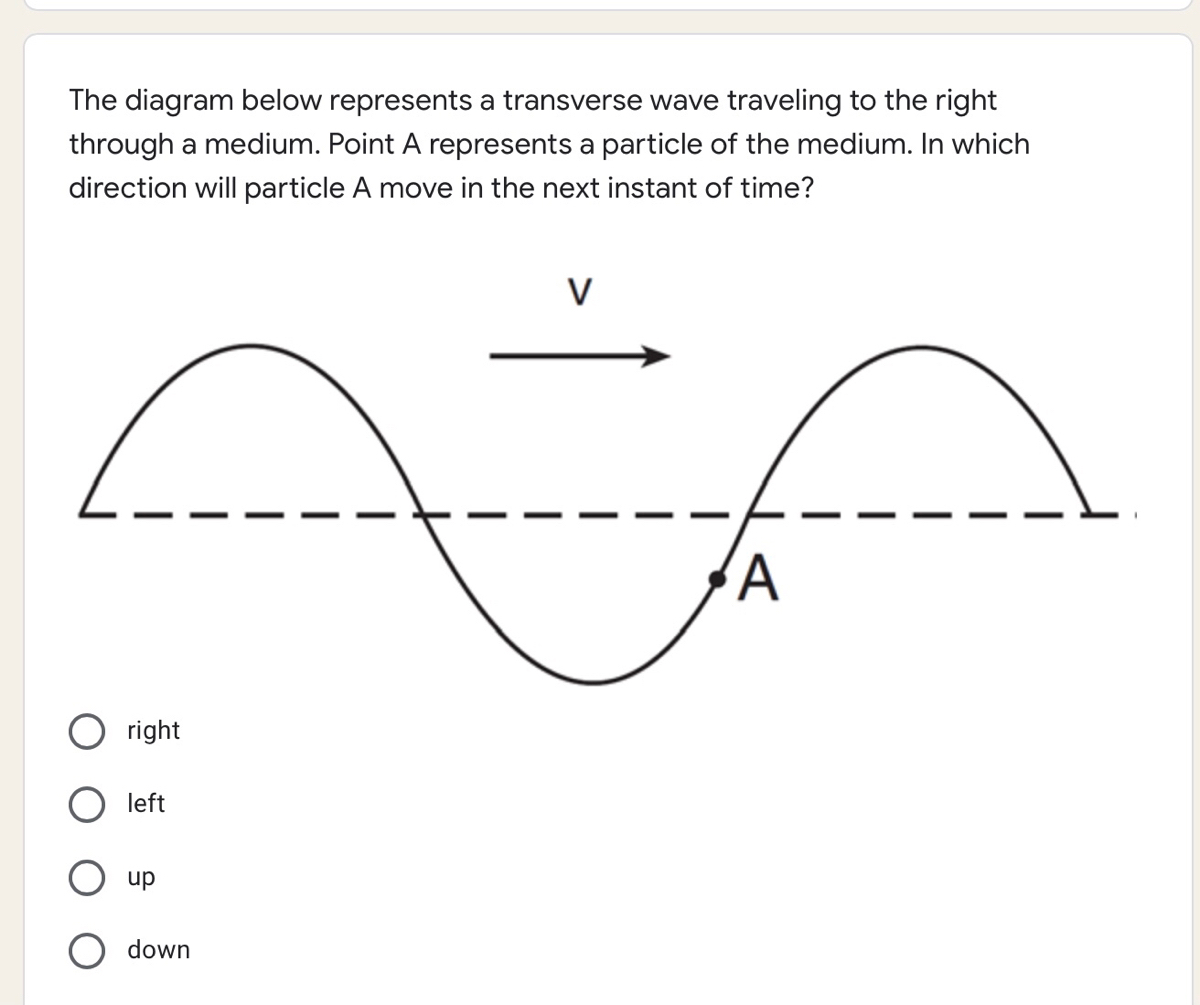
Answered The diagram below represents a… bartleby
In the diagram the rope moves up and down, producing peaks and troughs. Energy is transferred from left to right. However, none of the particles are transported along a transverse wave. The.

Anatomy of a Transverse Wave? YouTube
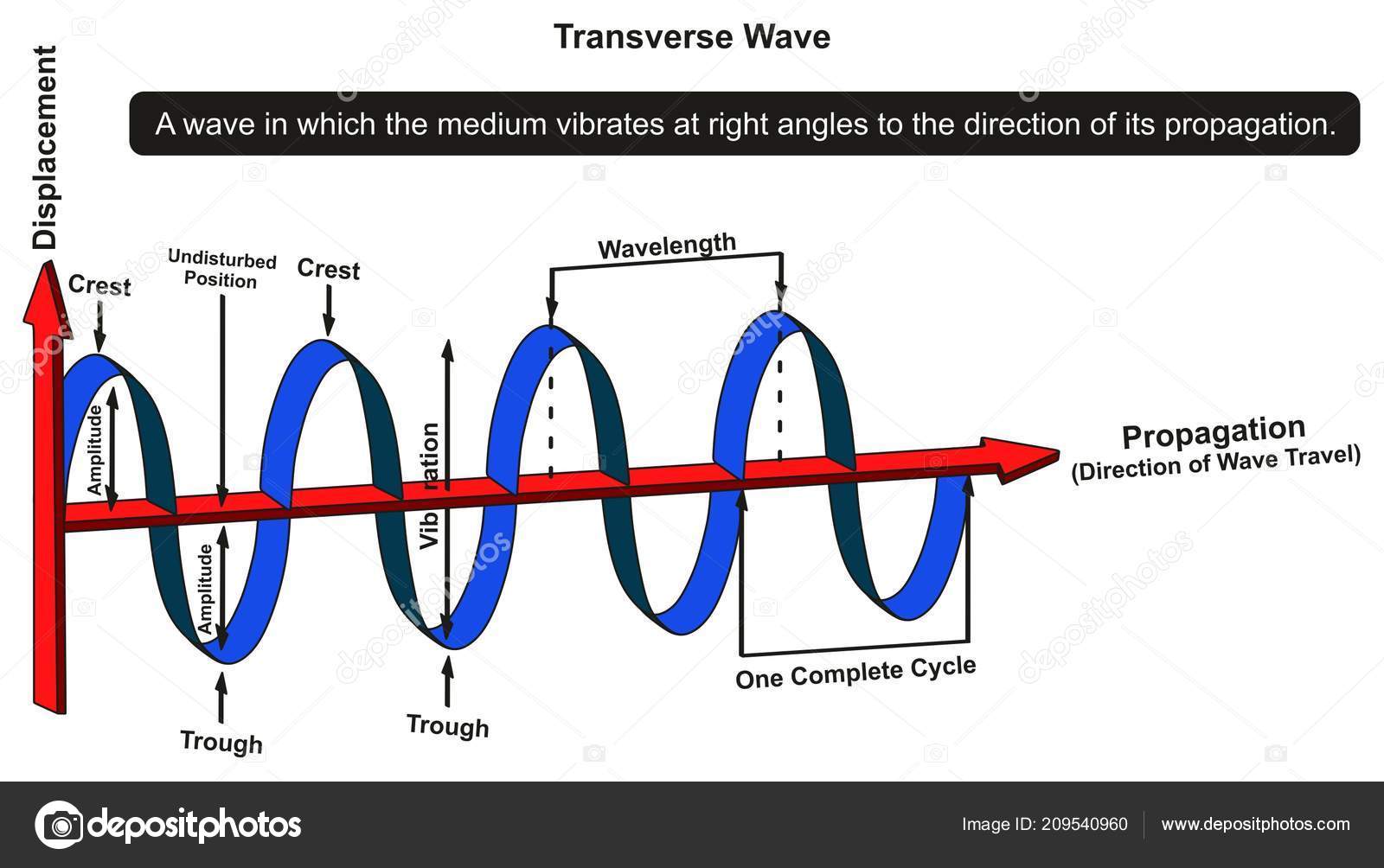
Category: Science & Tech Related Topics: transverse wave, motion in which all points on a wave oscillate along paths at right angles to the direction of the wave's advance. Surface ripples on water, seismic S (secondary) waves, and electromagnetic ( e.g., radio and light) waves are examples of transverse waves.
Transverse Wave Infographic Diagram Showing Structure Displacement Propagation Axis All Stock
A transverse wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium are displaced in a direction perpendicular to the direction of energy transport. A transverse wave can be created in a rope if the rope is stretched out horizontally and the end is vibrated back-and-forth in a vertical direction.

Transverse Wave Diagram Crest Trough Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 2121708785 Shutterstock
Figure 1.2.1b - Snapshot of a Periodic Wave. The second way to determine if a wave is periodic is mathematical. The function repeats itself upon translation by a certain distance in the ± x direction. That is: f(x ± vt) = f(x ± vt ± nλ), n = 0, 1, 2,.. The quantity λ is the length of the repeating waveform, and is called the.
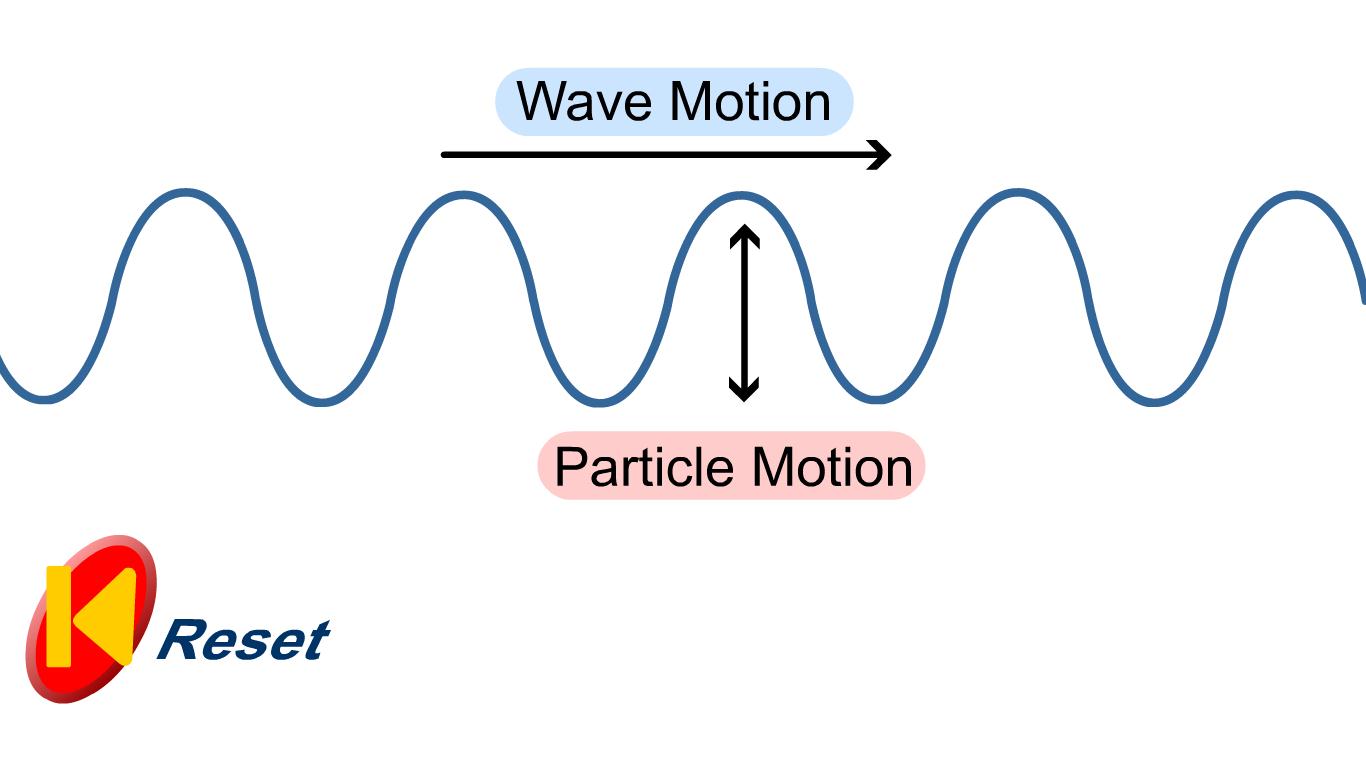
Frazer does Physics 3.2 Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
In the diagram the rope moves up and down, producing peaks and troughs. Energy is transferred from left to right. However, none of the particles are transported along a transverse wave. The.
[Solved] 1. What is a transverse wave? Draw one and label the... Course Hero
In Physics, waves are explained as an oscillation about the fixed point, accompanied by the transfer of energy travelling from one medium to another. When energy transfer occurs through a medium due to oscillation, the resultant wave can be termed a mechanical wave. The medium of transmission limits the distance of the wave's propagation.
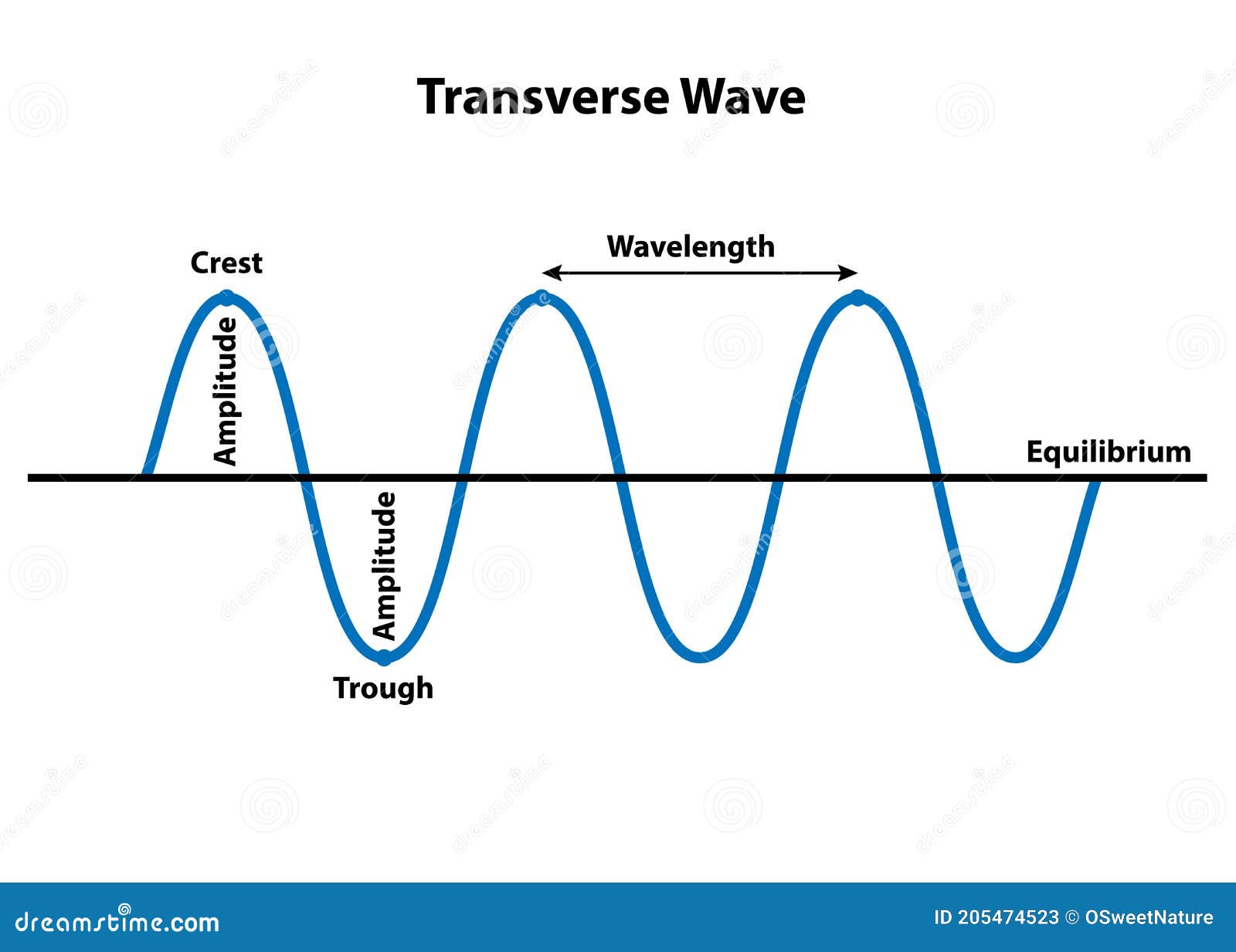
Transverse Wave Properties of Wavelength Stock Vector Illustration of science, form 205474523
Transverse and longitudinal waves are two types of mechanical waves, which involve the transfer of energy through a medium (e.g. water, air, a solid). Learn about transverse and longitudinal waves through the examples of a shaken rope and a sound wave. Finally learn about the difference between a single wave pulse and periodic waves.
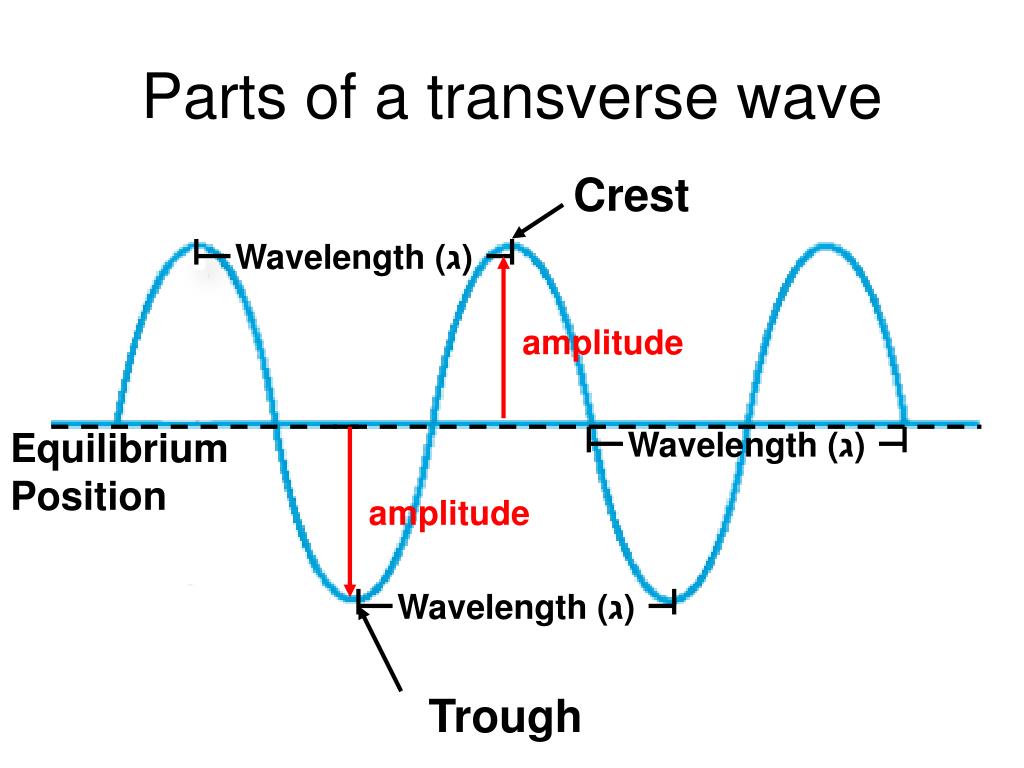
PPT Waves and Sound PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6313258
Tutorial 1.3: Transverse Waves. Transverse waves are the kind of wave you usually think of when you think of a wave. The motion of the material constituting the wave is up and down so that as the wave moves forward the material moves perpendicular (or transverse) to the direction the wave moves.Examples of transverse waves include waves on a string and electromagnetic waves.
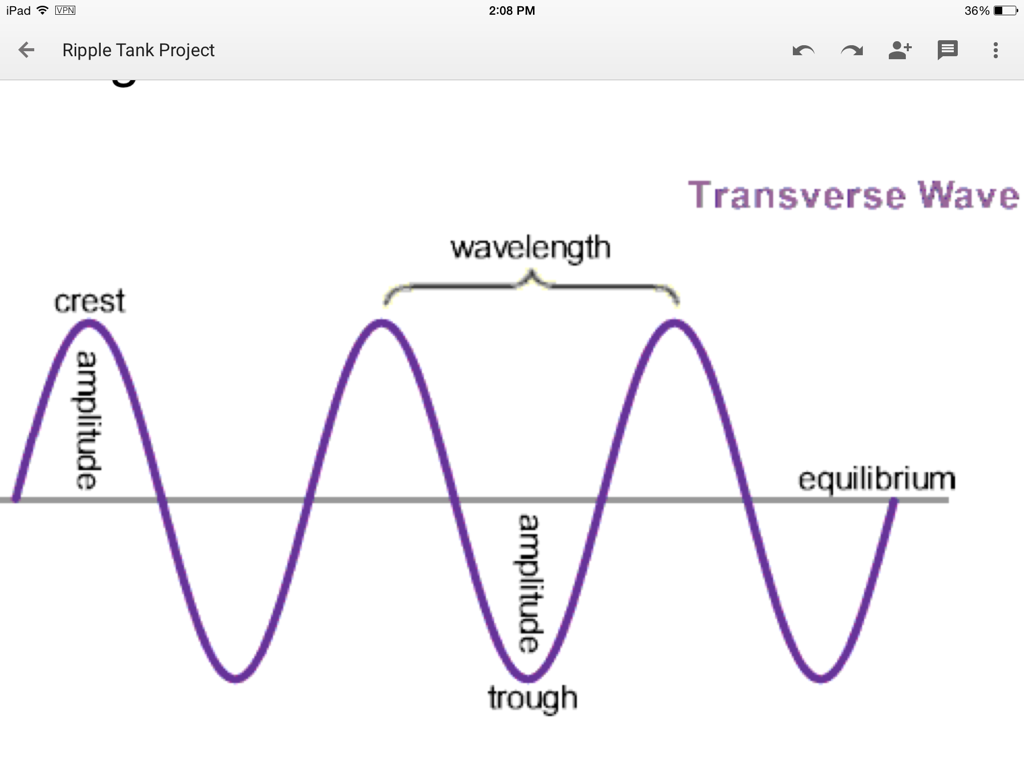
Waves Part 1
To Do 1: Press the white bottom to start. Switch S1 down to Pulse mode. Adjust the knobs of Amplitude and Frequency the way you can see clearly a pulse of wave. Vary kindly the Amplitude and Frequency and notice the difference on the pulse shape. To Do 2: Switch S1 down to Wave mode.

PPT Wave Top 12! PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2622129
In a transverse wave, the particles are displaced perpendicular to the direction the wave travels. Examples of transverse waves include vibrations on a string and ripples on the surface of water. We can make a horizontal transverse wave by moving the slinky vertically up and down.

PPT VIBRATIONS AND WAVES PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4613430
In Physics, a transverse wave is a moving wave whose oscillations are perpendicular to the direction of the wave. A simple demonstration of the wave can be created on a horizontal length of the string by securing one end of the string and moving the other up and down.